TradeStream
Trade Stream is a gRPC-based trading platform that allows users to execute stock trades and receive real-time price updates with high efficiency and low latency.
🔗Github Link
Technologies Used: Spring Boot, gRPC, H2 DB, JPA
Features
- Real-Time Stock Trading: Enables users to buy and sell stocks seamlessly, with instant price retrieval and trade execution.
- Live Price Updates: Provides continuous streaming of real-time stock price updates, allowing users to monitor market fluctuations instantly.
- User-Centric Design: Supports a smooth user experience by handling all backend processes, including price fetching and balance updates, without requiring frontend input for pricing.
- Scalable gRPC Architecture: Leverages gRPC for efficient, low-latency communication between microservices, ensuring quick and reliable data transmission.
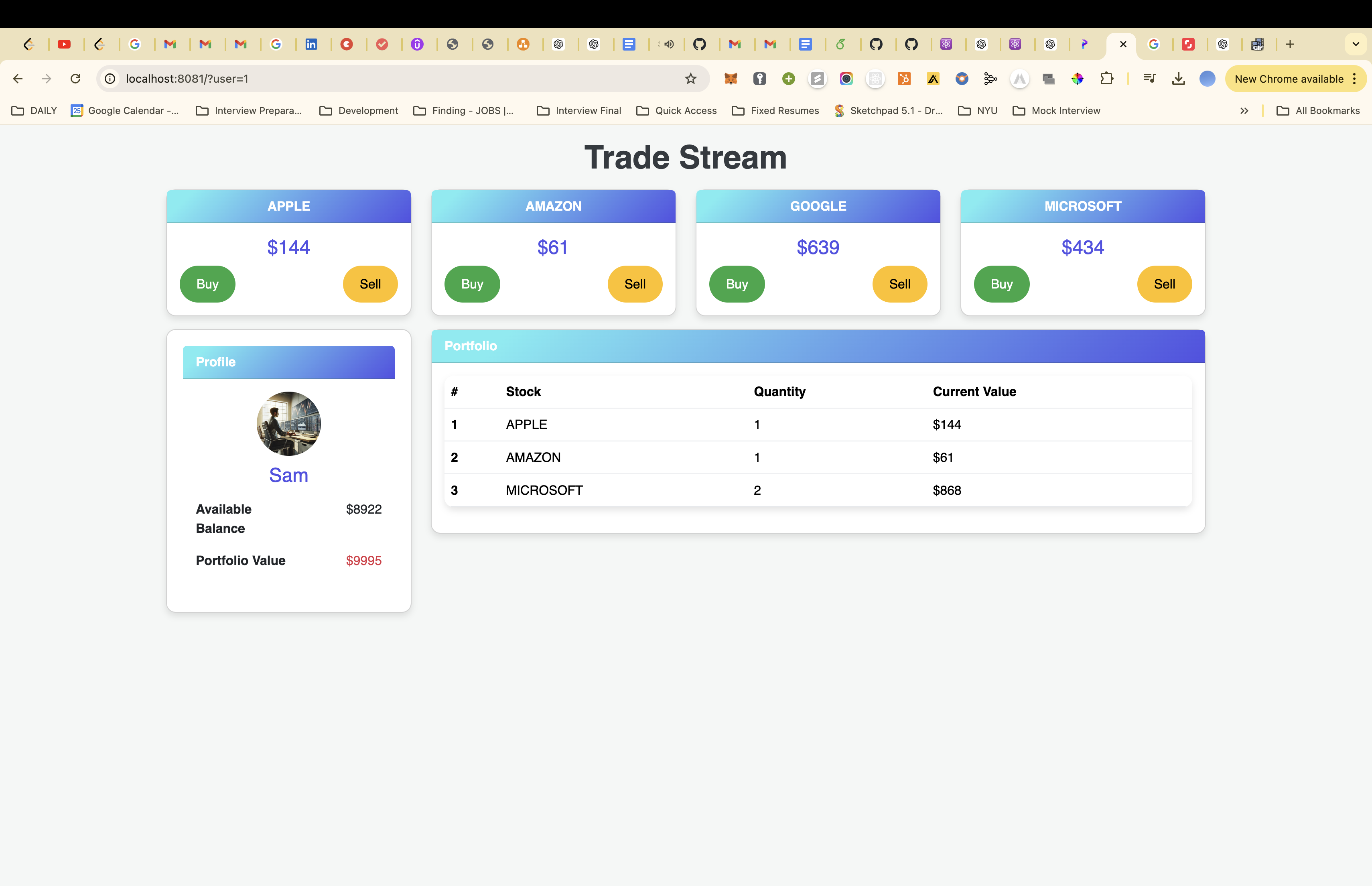
Make Trade - Architecture
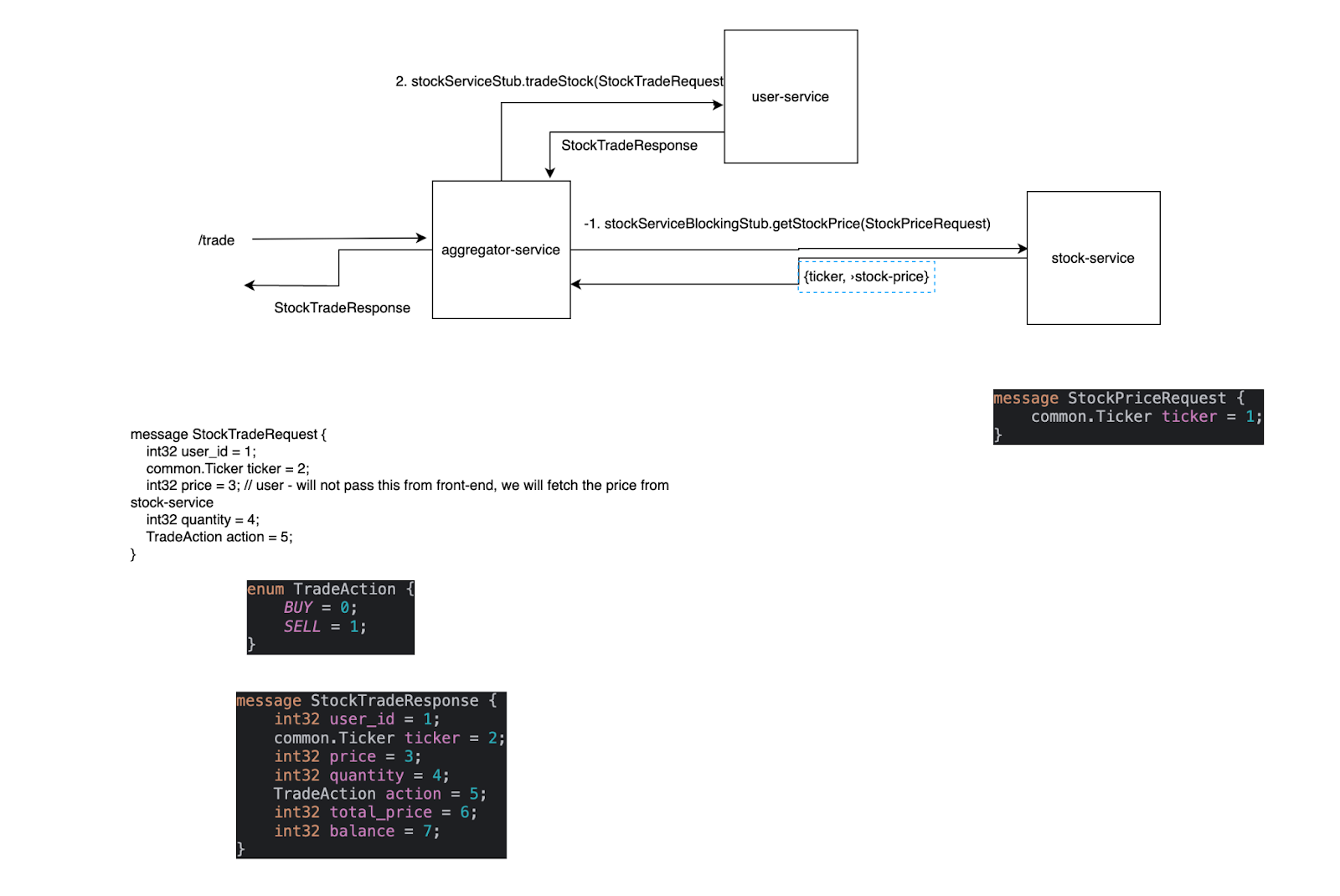
The stock trading service in “Trade Stream” enables users to buy and sell stocks through a streamlined gRPC-based communication system. The service is designed to interact with multiple microservices to ensure accurate price fetching, secure trading, and responsive feedback to the user.
Architecture Explanation:
-
User Request Initiation:
- The process starts when a user sends a trade request to the aggregator-service via the
/tradeendpoint. The request contains crucial information such as theuser_id,ticker,quantity, and the action (BUYorSELL).
- The process starts when a user sends a trade request to the aggregator-service via the
-
Price Fetching:
-
Since the price is not directly passed from the frontend, the aggregator-service first interacts with the stock-service to fetch the current price of the stock. This is done through a synchronous gRPC call using the
stockServiceBlockingStub.getStockPricemethod, passing aStockPriceRequestthat includes the stock’sticker. -
The stock-service processes the
StockPriceRequestand returns the stock’s current price, which is then used by the aggregator-service to complete the trade.
-
-
Trade Execution:
-
With the fetched price, the aggregator-service constructs a
StockTradeRequestand invokes thestockServiceStub.tradeStockmethod. This gRPC call triggers the actual trade process, which involves updating user data and the stock inventory in the user-service. -
The user-service processes the trade by adjusting the user’s balance and stock holdings according to the action (
BUYorSELL), and returns aStockTradeResponseto the aggregator-service. This response contains the updated details, including the total price of the trade and the user’s remaining balance.
-
-
Response to User:
- Finally, the aggregator-service sends a
StockTradeResponseback to the user, confirming the success of the transaction along with details such as the trade price, total cost, and updated balance.
- Finally, the aggregator-service sends a
Key Protobuf Definitions:
-
StockTradeRequest: Contains fields likeuser_id,ticker,price,quantity, andTradeAction(eitherBUYorSELL). -
TradeAction: Enum defining the possible actions (BUYorSELL). -
StockTradeResponse: Returns the trade details, including total price and updated balance.
Price Update Streaming- Architecture
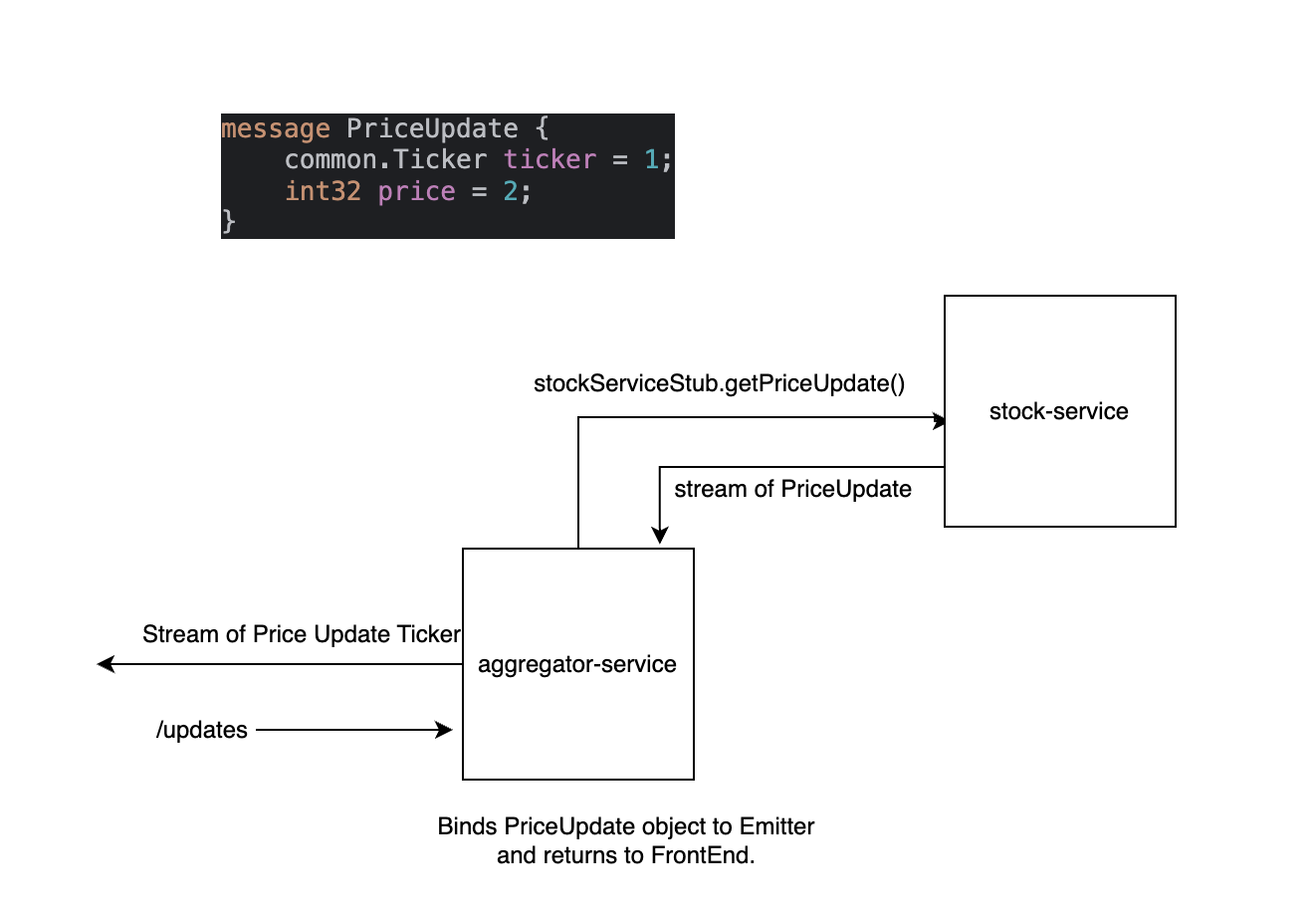
The stock trading service in “Trade Stream” enables users to buy and sell stocks through a streamlined gRPC-based communication system. The service is designed to interact with multiple microservices to ensure accurate price fetching, secure trading, and responsive feedback to the user.
Architecture Explanation:
-
User Request Initiation:
- The process starts when a user sends a trade request to the aggregator-service via the
/tradeendpoint. The request contains crucial information such as theuser_id,ticker,quantity, and the action (BUYorSELL).
- The process starts when a user sends a trade request to the aggregator-service via the
-
Price Fetching:
-
Since the price is not directly passed from the frontend, the aggregator-service first interacts with the stock-service to fetch the current price of the stock. This is done through a synchronous gRPC call using the
stockServiceBlockingStub.getStockPricemethod, passing aStockPriceRequestthat includes the stock’sticker. -
The stock-service processes the
StockPriceRequestand returns the stock’s current price, which is then used by the aggregator-service to complete the trade.
-
-
Trade Execution:
-
With the fetched price, the aggregator-service constructs a
StockTradeRequestand invokes thestockServiceStub.tradeStockmethod. This gRPC call triggers the actual trade process, which involves updating user data and the stock inventory in the user-service. -
The user-service processes the trade by adjusting the user’s balance and stock holdings according to the action (
BUYorSELL), and returns aStockTradeResponseto the aggregator-service. This response contains the updated details, including the total price of the trade and the user’s remaining balance.
-
-
Response to User:
- Finally, the aggregator-service sends a
StockTradeResponseback to the user, confirming the success of the transaction along with details such as the trade price, total cost, and updated balance.
- Finally, the aggregator-service sends a
Key Protobuf Definitions:
-
StockTradeRequest: Contains fields likeuser_id,ticker,price,quantity, andTradeAction(eitherBUYorSELL). -
TradeAction: Enum defining the possible actions (BUYorSELL). -
StockTradeResponse: Returns the trade details, including total price and updated balance.
Motivation
The motivation behind the Trade Stream project was to empower individual investors by providing them with a real-time trading platform that combines ease of use with powerful functionality. Additionally, it served as a learning opportunity to explore and implement gRPC and microservices for efficient, scalable communication in financial applications.